Plant This, Not That:
Native Alternatives to Common Landscaping Plants
Presented by Valerie Malaney
We Are Losing the Little Things that Run our World!
How big is the problem?
- Up to 90% of the Eastern Monarch butterfly population is in decline
- 40% of our pollinators, including the bees, are in decline
- 3 billion birds have disappeared in the last 30 years
- 1 Million Species extinct in the next few decades
- Deemed the 6th Mass Extinction on the Planet
The Reason We Are Losing Biodiversity
- Habitat Loss
-
-
- Over 40 million acres lawn
- 38% Planet Land- Agriculture
-
- Plant Choice
- Pesticides
- Neonicotinoids kills butterflies, bees and birds
- Mosquito spray kills +++
- Herbicides
- Like Round-up
- Light Pollution
- Invasive Species
- New Diseases
- Climate Change Challenges
Traditional Horticulture – Shift to Ecological Horticulture
Tidy, Trendy, Showy Biodiversity, Habitat, Life Sustaining
Let’s Plant!
Terminology
Native: co-evolved with the local flora and fauna, thus serving ecological services
Non-native: not historically present, brought through human intervention (Another continent, climate, physical separation)
Invasive: introduce via humans and causing harm to natural areas
Aggressive: Native but strong ability to spread rapidly via rhizomes or seed dispersal
Cultivar: Horticultural practice of breeding or cloning for specific traits, patentable Hydrangea arborescens ‘Annabelle’
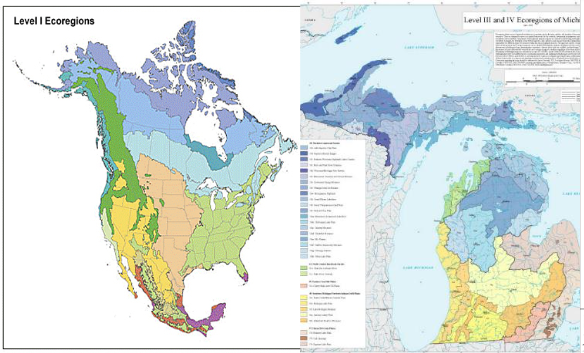
EcoRegions, not Hardiness Zones
Eastern Temperate Forest Interlobate Dead Ice Moraine
EPA EcoRegion Maps EPA EcoRegion Map
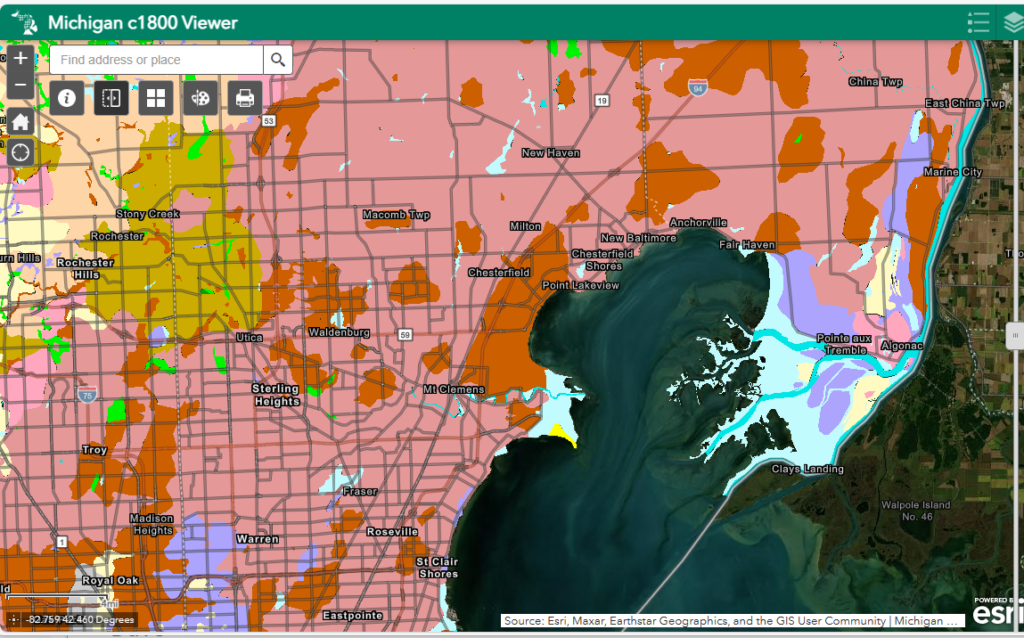
Black Oak Barren Oakland County Circa 1800
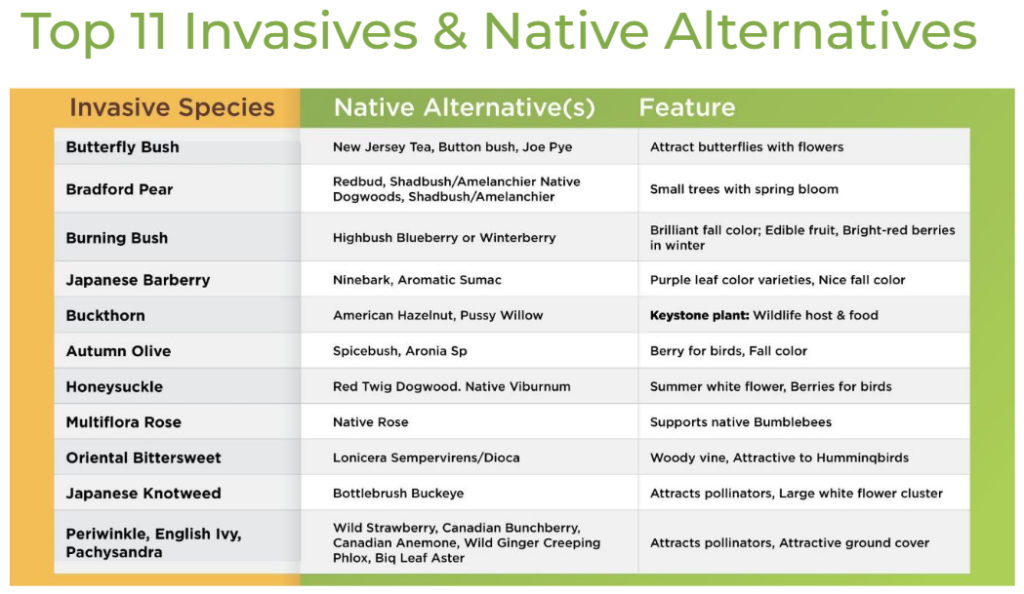
Additional Examples:
Burning Bush – Euonymus alatus – Invasive
Native: Euonymus obovatus or atropurpureus, Winterberry/Ilex sp, Red Twig Dogwood/Silky Dogwood/Swida (Cornus sp), Fragrant Sumac/Rhus aromatica, Viburnum sp (Maple leaf, Nannyberry, etc), Chokeberry / Aronia sp, Chokecherry – Prunus
Japanese Barberry – Berberis – Invasive Barberry Alternatives (habitatmatters.org)
Native: Blueberry/Vaccinium, New Jersey Tea – Ceanothus, Leadplant/Amorpha, Bush Honeysuckle/Diervilla lonicera, Ninebark/Physocarpus
Butterfly Bush – Buddleja – Invasive (no caterpillars)
Native: Ironweed/Vernonia, JoePye/Eutrochium, Buttonbush/Cephalanthus, Milkweed/Asclepias (12 species in MI), Phlox sp (5 species NE)
Native Alternatives to Autumn Olive
Mistaken Monday:
Go Beyond Beauty Campaign
Landscape Alternatives 2023.pdf (bugwoodcloud.org)
Invasive/Non-Native Native Alternative
Purple Loosestrife Fireweed
Orange Daylily Michigan Lily
Yellow Flag Iris Native Blue Flag Iris/s
Wintercreeper Partridge berry
Dame’s Rocket Woodland Phlox
Common St. John’s wort Shrubby St John’s wort
Norway Maple Sugar Maple
Callery Pear Allegheny Serviceberry
Callery Pear Chokecherry/Black Cherry
Tree-of-Heaven Staghorn Sumac
Common Buckthorn Black Chokeberry
Multiflora Rose Carolina Rose
Invasive Groundcovers to avoid:
Lily of the Valley, Snow on the Mountain, Creeping Jenny, Sweetwoodruff, Forget-me-not, English Ivy, Periwinkle
Native Groundcovers to use instead:
Wild Ginger, Bearberry, Wild Geranium, Fragrant Sumac (low grow cultivar), Wild Strawberry, Canada anemone, Sedges \
Vertical Flower Power!
Native Trees and Shrubs
70’ Black Cherry Tree = 3500 Sqft flowers
- American Basswood
- Elderberry
- Maples*
- Willows*
- Redbud*
- Tulip Poplar
- Black/Chokecherry
- Crabapple
- Dogwood
- Catalpa
- Spicebush*
- Viburnums
* Flower precedes leaves
Keystone Plants
“Essential members of every landscape.”
Doug Tallamy
University of Delaware
Keystone plants host the most caterpillars.
- Plants have chemical defenses
- Plants and insects evolved together
- Butterfly caterpillars are plant specific
- Not all plants are equal
So, if you want more butterflies, give their babies food…
Native Host Plants!
www.nwf.org/NativePlantFinder
Michigan Lepidoptera
100+ Butterflies
50+ Skippers
1000+ Moths
Many Different Host Plants!
Caterpillars convert the most plant biomass to animal biomass
Aphids are also important food web insects and are host plant specific! They are one of the best ways to bring in beneficial insects
Use the 10 Step method! If you are bothered by holes or insects on plants, take 10 steps back. If you are no longer bothered, leave it alone.
465 Michigan Native Bee Species
50% in severe decline
1 in 4 are Imperiled
(Center for Biological Diversity)
30% are Pollen Specialists
90% are Solitary
70% Ground nest
30% Cavity nest
Pithy Standing Stems more important than “Bee Hotels
Partial List of Plants that Provide the Natural Bee Homes
- Goldenrods (Solidago sp.)
- Purple Coneflower (Echinacea sp.)
- Milkweed (Asclepias sp.)
- Blazing Star (Liatris sp)
- Rose Mallow (Hibiscus sp)
- Wild Bergamot (Monarda sp)
- Joe Pye Weed (Eutrochium sp)
- Sumacs (Rhus sp)
- Elderberry (Sambucus sp)
- Cup Plant (Silphium sp)
- Culver’s Root (Veronicastrum sp)
- Boneset (Eupatorium sp)
- Blue Wild Indigo (Baptisia sp)
- Native Raspberry (Rubus sp)
- Bunching Grasses…
Plant Recommendations for Soil Sun Conditions
Resources:
- DOUG TALLAMY PhD (Founder of the backyard native plant movement)
- “Nature’s Best Hope” Book
- “The Nature of Oaks” Book
- YouTube Channel
- Put your garden on the map
- NWF – Native Plant Finder – Zip code
- Michigan Flora – is the plant native to MI?
- Raising Butterflies in the Garden
- Brenda Dziedzic (Michigan)
- HEATHER HOLM
Pollinatorsnativeplants.com